Unlocking the core question
Profit margins are a key indicator of a business’s financial performance and efficiency. They provide insight into how well a company is managing its costs and generating profits from its operations. Profit margins are typically expressed as a percentage and represent the relationship between a company’s net profit and its revenue. There are several types of profit margins, including gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, each offering a different perspective on financial performance.
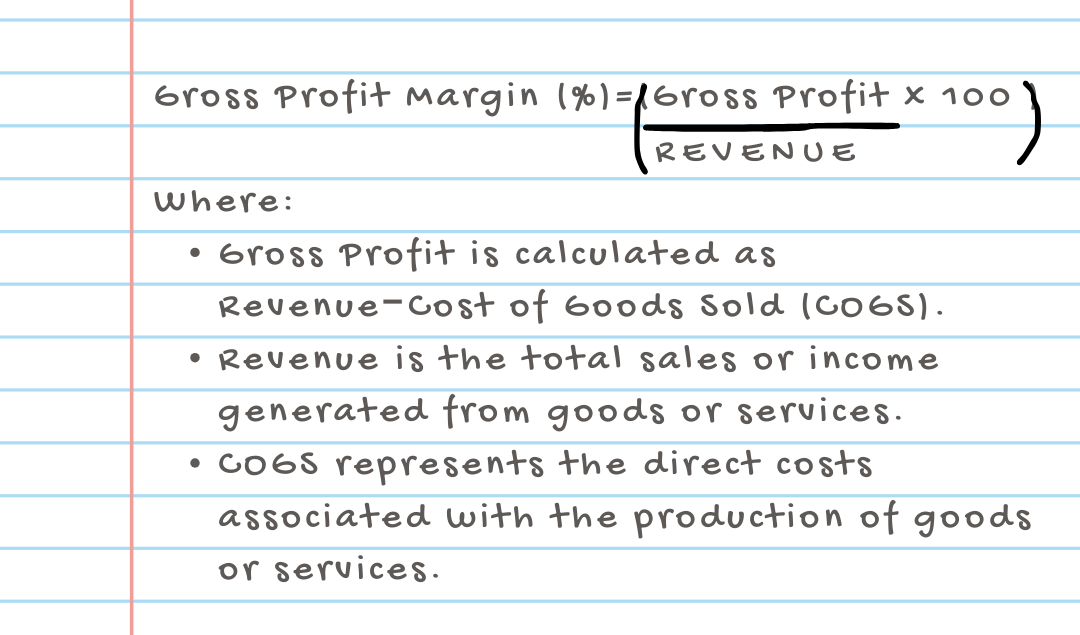
a.) Gross Profit Margin
- This margin measures the profitability of a company’s core business activities.
- A higher gross profit margin indicates that the company is efficiently producing and selling its product.

b.) Operating Profit Margin
- This margin reflects the company’s ability to generate profit from its core operations.
- It considers operating expenses, providing insight into the efficiency of day-to-day operations.


c.) Net Profit Margin
- This margin assesses the overall profitability of the business after considering all expenses, including taxes and interest.
- It provides a comprehensive view of the company’s ability to manage costs and generate profits.


Interpretation:
- High Profit Margins: Generally, high profit margins indicate that a company is effectively controlling its costs and is efficient in generating profits from its operations.
- Low Profit Margins: Lower margins may suggest that a company is struggling to control costs or facing challenges in pricing and sales.
- Industry Comparison: Profit margins are often more meaningful when compared to industry benchmarks. What might be considered a healthy margin in one industry may be low in another.
- Trends Over Time: Examining profit margins over time helps identify patterns and assess the impact of strategic decisions on a company’s financial health.
It’s important to note that profit margins should be analyzed in conjunction with other financial metrics and industry benchmarks for a comprehensive understanding of a business’s financial performance. Additionally, profit margins alone may not provide a complete picture, and other factors such as cash flow, debt levels, and market conditions should also be considered.
FAQs
Q: Can a business survive with low profit margins?
A: While challenging, businesses with low profit margins can survive by focusing on volume, cost optimization, and strategic alliances.
Q: Are there industry-specific benchmarks for profit margins?
A: Yes, industries vary, and it’s essential to compare profit margins within the same sector for accurate analysis.
Q: How often should a business analyze its profit margins?
A: Regular analysis, at least quarterly, ensures timely identification of trends and facilitates proactive decision-making.
Q: Can external factors impact profit margins overnight?
A: Yes, sudden market shifts, geopolitical events, or regulatory changes can swiftly influence profit margins.
Q: What role do technological advancements play in improving profit margins?
A: Embracing technology can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and positively impact profit margins in the long run.
Q: Is gross profit margin more critical than net profit margin?
A: Both are vital; gross margin reflects core profitability, while net margin considers overall business expenses.
Q: Why are profit margins important for businesses?
A: Profit margins provide insights into a company’s efficiency, competitiveness, and sustainability, crucial for stakeholders and investors.
Q: How can a business improve its profit margins?
A: Implementing cost-cutting measures, revenue enhancement tactics, and focusing on operational efficiency are effective strategies.
Q: What role do economic factors play in profit margin analysis?
A: Economic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, can impact profit margins, requiring businesses to adapt to changes.
Q: Why is benchmarking profit margins against industry standards essential?
A: Benchmarking helps businesses understand their position in the market and identify areas for improvement.
Q: How can businesses avoid common pitfalls in profit margin analysis?
A: Avoiding pitfalls involves considering indirect costs, maintaining a balance between revenue and costs, and adopting a long-term focus.
You can also read importance of emergency fund in 2024.



Pingback: Mastering Cashflow Analysis In Accounting; A Complete Guide » Moneyfinacc.com